接前面PySide6下PyVista小记,简单看看PyVista的用法。
简单几何对象(Geometric Objects)
对于常见了简单几何对象,PyVista提供了高层次封装的方法。
二维对象
对于2D形状:圆弧、圆盘、圆、线、折线、多边形、平面
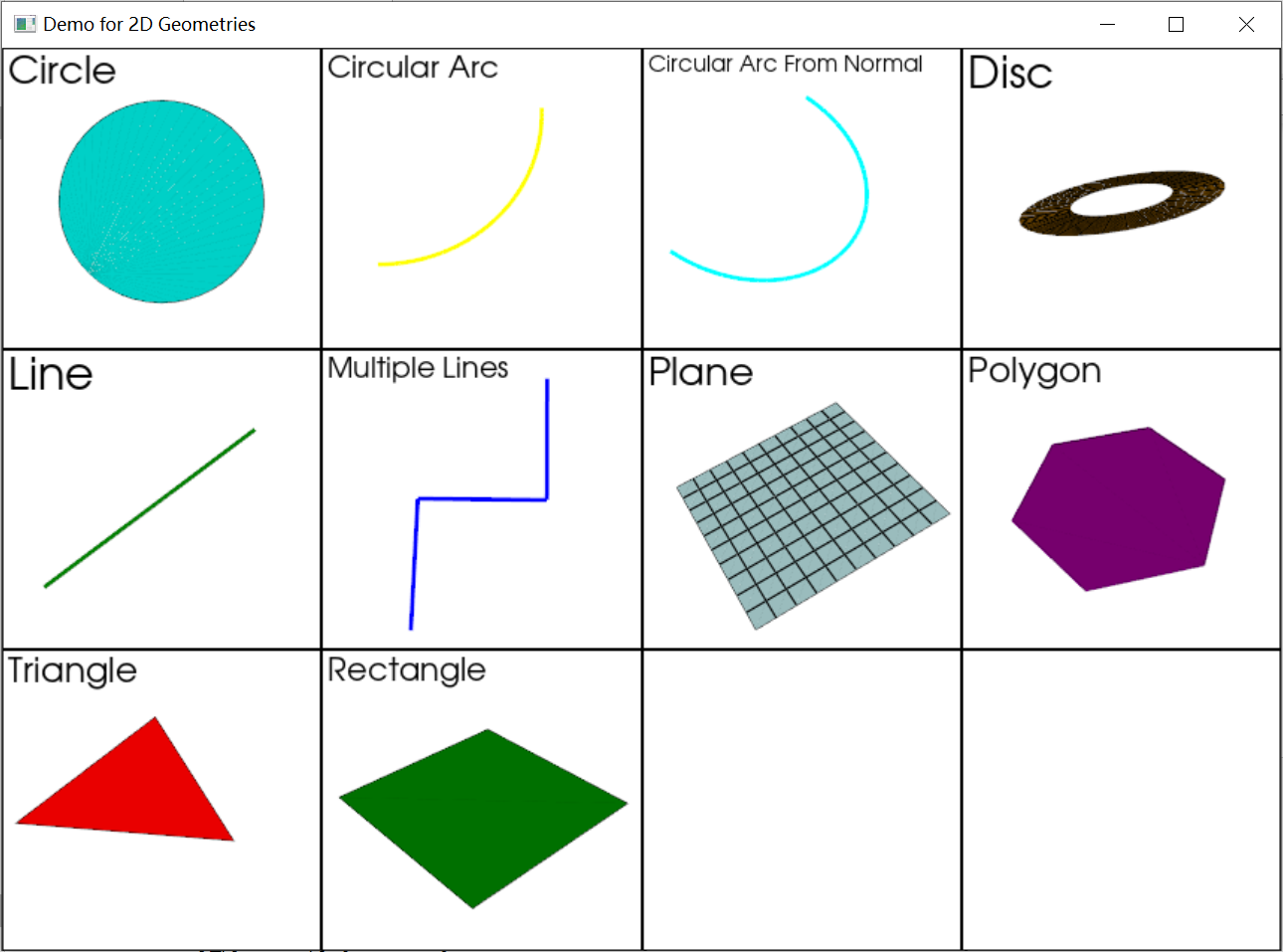
Circle([radius, resolution]): 创建一个平面上的圆形。CircularArc(pointa, pointb, center[, ...]): 创建一个由两个端点和中心定义的圆弧。CircularArcFromNormal(center[, resolution, ...]): 创建一个与法线平面相切的圆弧。Disc([center, inner, outer, normal, r_res, ...]): 创建一个带孔的二维圆盘。Line([pointa, pointb, resolution]): 创建一条线段。Plane([center, direction, i_size, j_size, ...]): 创建一个平面,尽管是3D空间中的对象,但通常在二维几何中处理,定义了一个无限平面。Triangle([[points]]): 创建三级形Rectangle([[points]]): 创建矩形MultipleLines([points]): 创建多条线,属于二维。Polygon([center, radius, normal, n_sides, fill]): 创建一个多边形。
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 | |
三维对象
有点多,分成两部分:
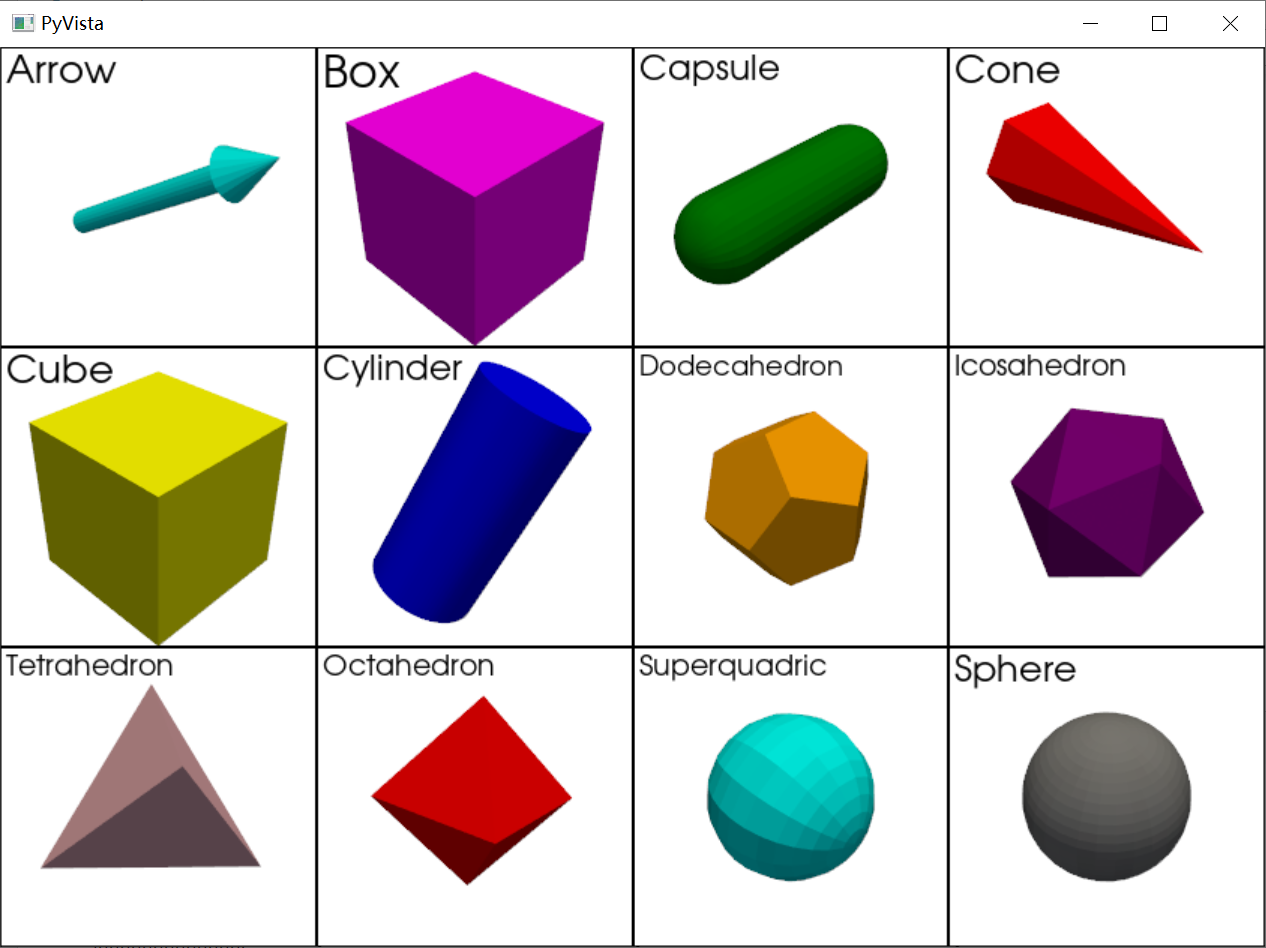
Arrow([start, direction, tip_length, ...]): 创建一个箭头Box([bounds, level, quads]): 创建一个具有固体面的盒子Capsule([center, direction, radius, ...]): 创建胶囊体Cone([center, direction, height, radius, ...]): 创建一个圆锥体Cube([center, x_length, y_length, z_length, ...]): 创建一个立方体Cylinder([center, direction, radius, ...]): 创建一个圆柱体的表面CylinderStructured([radius, height, center, ...]): 创建一个圆柱体网* `格,属于三维。Dodecahedron([radius, center]): 创建一个十二面体Icosahedron([radius, center]): 创建一个二十面体Icosphere([radius, center, nsub]): 创建一个二十面体球Tetrahedron([radius, center]): 创建一个四面体Octahedron([radius, center]): 创建一个八面体Superquadric([center, scale, size, ...]): 创建一个超二次体Sphere([radius, center, direction, ...]): 创建一个球体
示例代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 | |
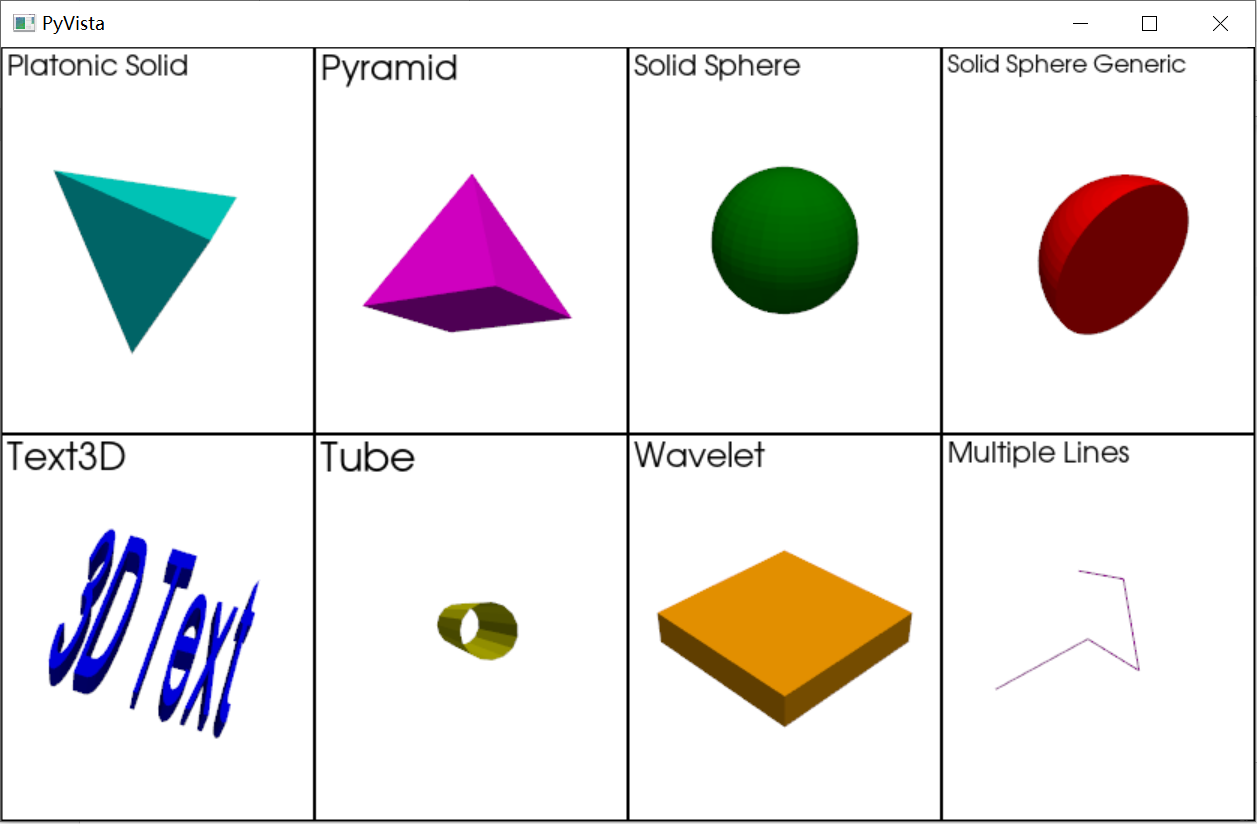
PlatonicSolid([kind, radius, center]): 创建一个柏拉图立体(正四、六、八、十二、二十)面体- 'tetrahedron'
- 'cube'
- 'octahedron'
- 'icosahedron'
- 'dodecahedron'
Pyramid([points]): 创建一个金字塔SolidSphere([outer_radius, inner_radius, ...]): 创建一个实心球SolidSphereGeneric([radius, theta, phi, ...]): 创建一个灵活采样的实心球 ,属于三维。Text3D(string[, depth, width, height, ...]): 创建三维文字Tube([pointa, pointb, resolution, radius, ...]): 创建一个管道Wavelet([extent, center, maximum, x_freq, ...]): 创建一个波形,有些复杂...
示例代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 | |
几何源(Geometric Sources)
几何源(Geometric Sources)更接近实际的 VTK 管道。它们在 VTK 管道中充当“源”节点,生成特定类型的几何体。
- 管道集成:这些源旨在集成到 VTK 管道中,其输出可以直接连接到其他管道阶段,如过滤器、映射器等。
- 精细控制:它们通常提供更多参数来控制几何体,更适用于需要对生成几何体进行细粒度控制的场景。
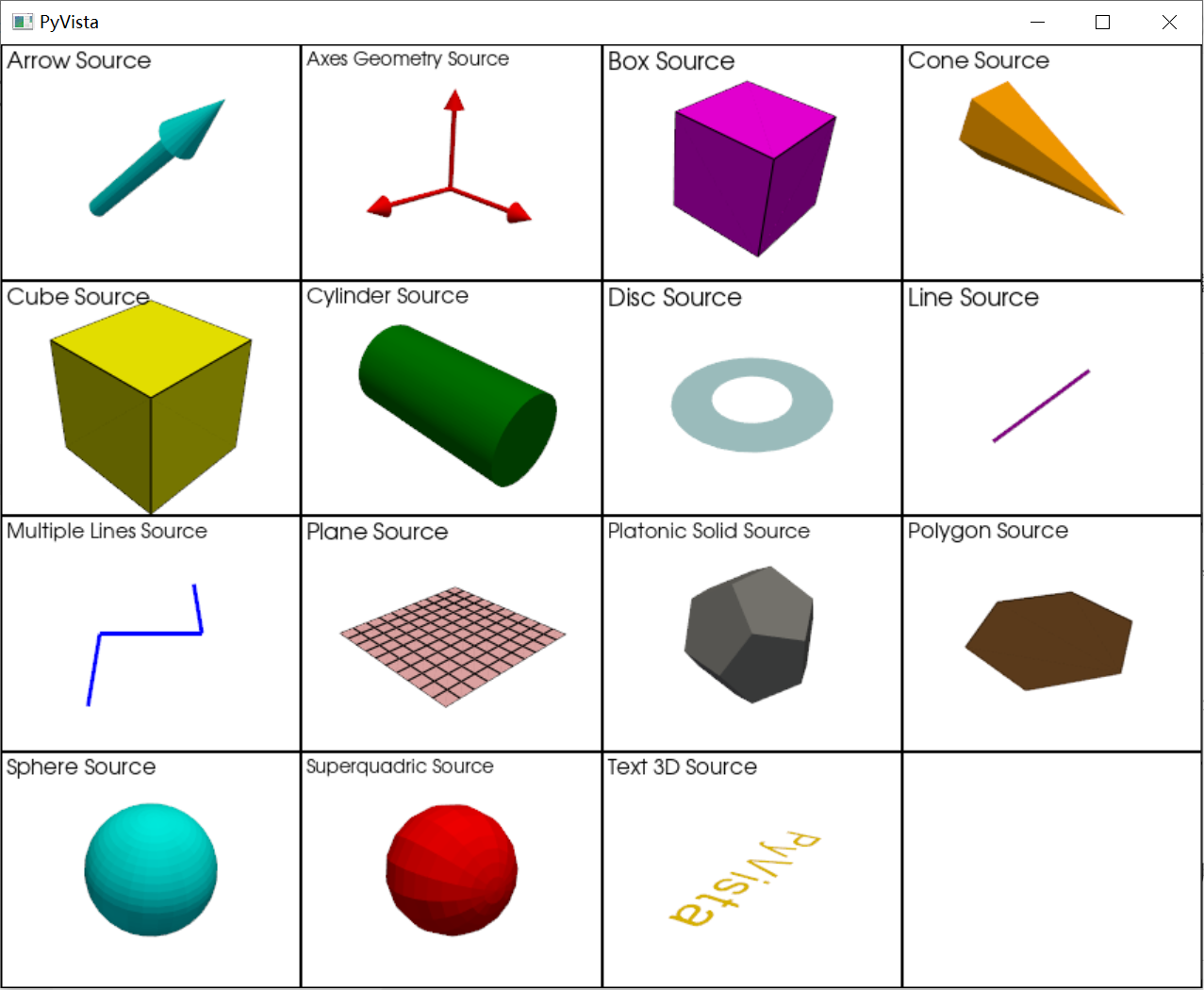
ArrowSource([tip_length, tip_radius, ...]):创建一个箭头源。AxesGeometrySource([[, shaft_type, ...]]):创建坐标轴几何源。注意和其他source的类型不同,需要调用 output。BoxSource([bounds, level, quads]):创建一个盒子源。ConeSource([center, direction, height, ...]):圆锥源算法类。CubeSource([center, x_length, y_length, ...]):立方体源算法类。CylinderSource([center, direction, radius, ...]):圆柱源算法类。DiscSource([center, inner, outer, r_res, c_res]):圆盘源算法类。LineSource([pointa, pointb, resolution]):创建一条线。MultipleLinesSource([points]):多条线源算法类。PlaneSource([i_resolution, j_resolution]):创建一个平面源。PlatonicSolidSource([kind]):柏拉图立体源算法类。(正四、六、八、十二、二十面体)PolygonSource([center, radius, normal, ...]):多边形源算法类。SphereSource([radius, center, ...]):球体源算法类。SuperquadricSource([center, scale, size, ...]):创建超二次曲面源。Text3DSource([string, depth, width, height, ...]):从字符串创建 3D 文字。
示例代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 | |
参数化几何对象(Parametric Geometric Objects)
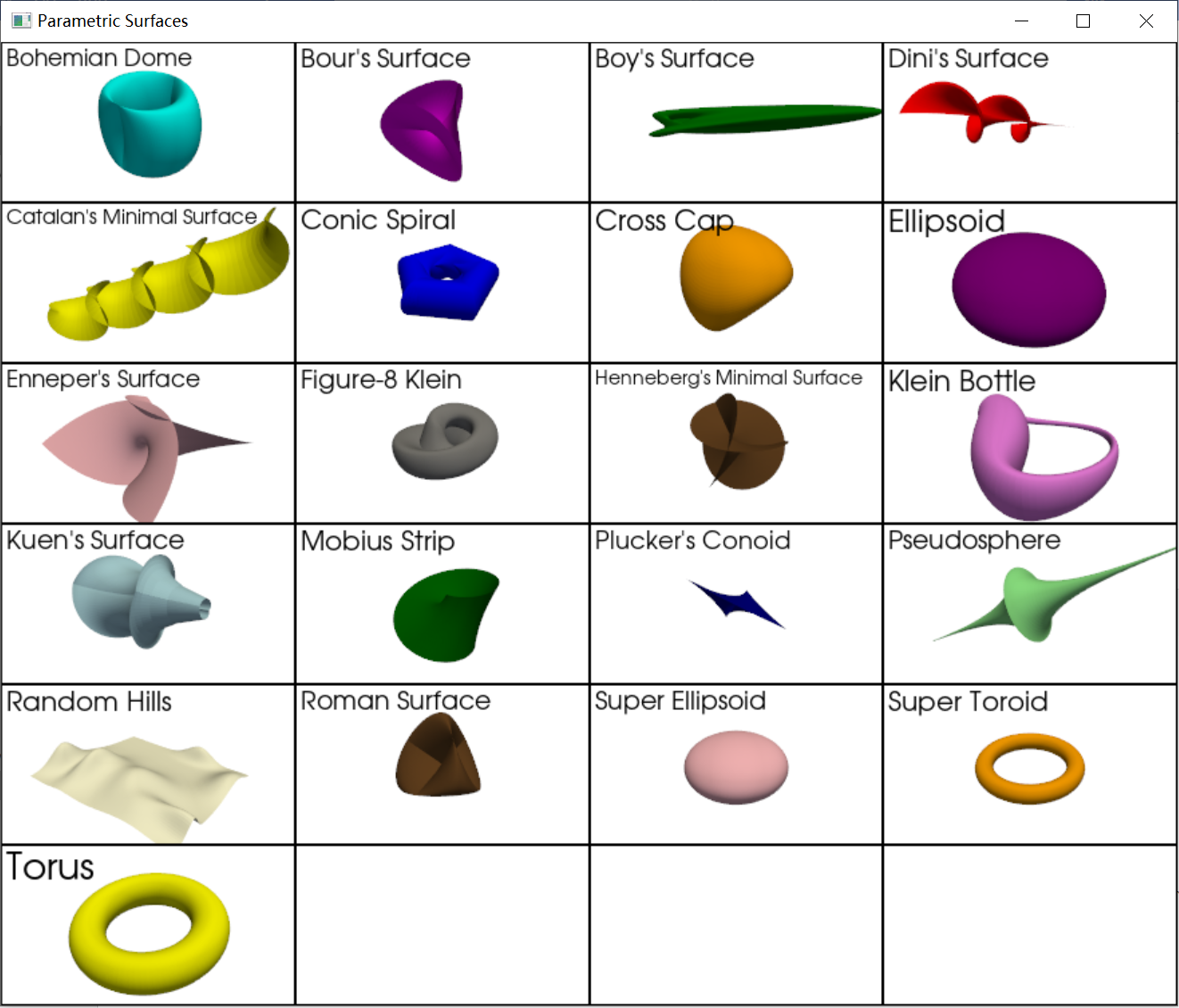
ParametricBohemianDome([a, b, c]): 生成波希米亚穹顶表面。ParametricBour(**kwargs): 生成布尔最小曲面。ParametricBoy([zscale]): 生成博伊曲面。ParametricDini([a, b]): 生成迪尼曲面。ParametricCatalanMinimal(**kwargs): 生成卡塔兰最小曲面。ParametricConicSpiral([a, b, c, n]): 生成类似海贝壳的圆锥螺旋曲面。ParametricCrossCap(**kwargs): 生成交叉帽。ParametricEllipsoid([xradius, yradius, zradius]): 生成椭圆体。ParametricEnneper(**kwargs): 生成恩内珀曲面。ParametricFigure8Klein([radius]): 生成8字型克莱因瓶。ParametricHenneberg(**kwargs): 生成亨内贝格最小曲面。ParametricKlein(**kwargs): 生成经典克莱因瓶表示。ParametricKuen([deltav0]): 生成库恩曲面。ParametricMobius([radius]): 生成莫比乌斯带。ParametricPluckerConoid([n]): 生成普吕克圆锥面。ParametricPseudosphere(**kwargs): 生成假球面。ParametricRandomHills([numberofhills, ...]): 生成覆盖随机山丘的曲面。ParametricRoman([radius]): 生成斯坦纳的罗马曲面。ParametricSuperEllipsoid([xradius, yradius, ...]): 生成超椭圆体。ParametricSuperToroid([ringradius, ...]): 生成超圆环。ParametricTorus([ringradius, crosssectionradius]): 生成圆环面。
示例代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 | |
数据模型(Data Model)
术语
似乎很乱!!
- DataObject:PyVista中所有数据集的 基类,负责提供内存管理、元数据管理和基本的操作接口,所有具体的数据集类型(如PolyData、ImageData等)都继承自DataObject。
- Data Sets:指的是PyVista中具体的几种数据类型,包括PolyData、StructuredGrid、UnstructuredGrid等,这些数据集包含点、单元格、拓扑等元素,表示不同的数据结构,用于存储几何信息。
- Point Sets:指的是包含离散点(例如顶点)的数据类型,通常用于表示几何物体的离散位置。PolyData是常见的点集数据集,它包含了点、线和面,可以表示复杂的三维几何形状。
- Gridded Data:指规则或非规则网格的数据集,包含在一个规则或不规则的网格上的数值。StructuredGrid、RectilinearGrid和ImageData都属于此类,适用于数据在一定范围内均匀或非均匀分布的情况,通常用于表示体积数据或网格计算结果。
- Composite Datasets:指由多个数据集组成的复合数据类型,允许存储多种不同数据集(如PolyData、ImageData等)并能够将它们组织成层次结构,MultiBlockDataSet是PyVista中常见的复合数据集类型,适用于复杂的多阶段数据分析。
数据集类(Data Sets)
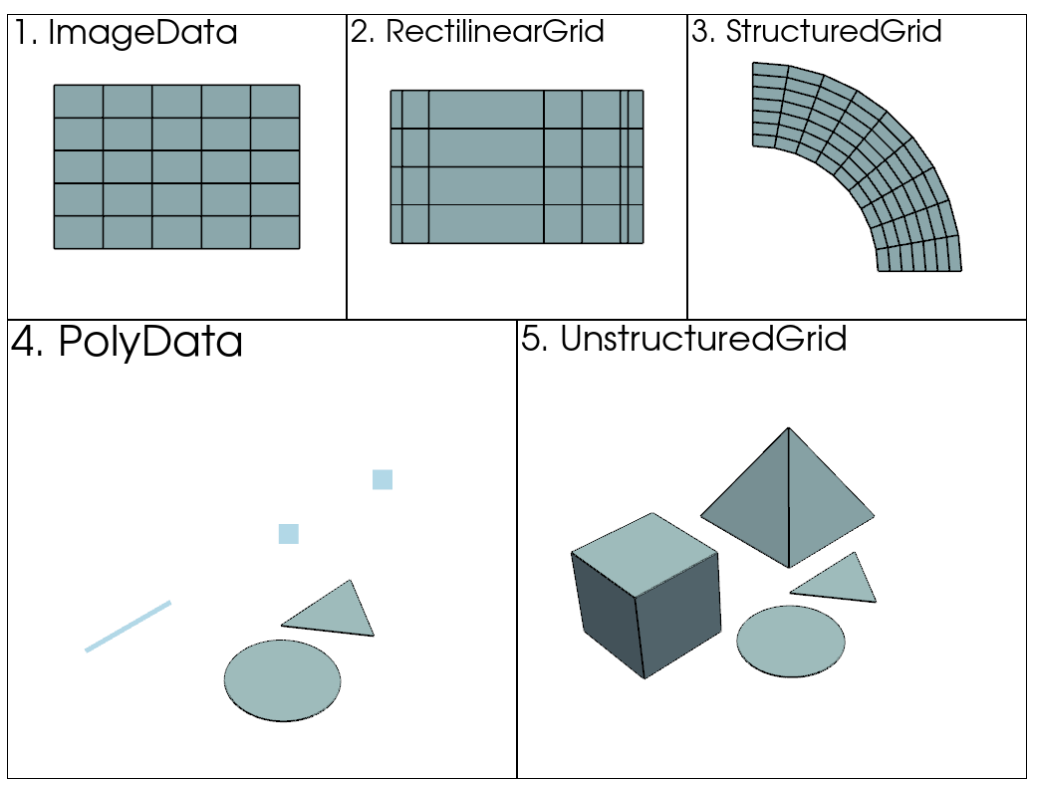
- ImageData:用于表示规则的数据,如医学图像或科学计算中的体积数据,适合存储像素或体素值。
- RectilinearGrid:用于规则网格,但每个维度的坐标可以不同,适用于不均匀坐标分布的网格。
- StructuredGrid:用于规则的网格数据,常用于科学计算,如气象和地质数据。
- PolyData:用于表示 二维 多边形数据,如点云、线段、面等,适合表示曲面模型。Poly是多边形的意思。
- UnstructuredGrid:用于表示不规则网格,支持任意类型的单元,适合复杂计算和仿真应用。
以上数据集按复杂度从低到高(1到5)排序。也就是说,每个数据集都可以表示为一个UnstructuredGrid,但UnstructuredGrid类需要最多的内存来存储,因为它必须考虑每个单独的点和单元。另一方面,由于vtkImageData(ImageData)是均匀间隔的,几个整数和浮点数就可以描述其形状,因此它需要最少的内存来存储。
属性(Attributes)
首先,区分点和单元的概念:
- 点 (Points) 表示位置或坐标,是单独的空间元素。
- 单元 (Cells) 是由多个点组合而成的几何单元,定义了网格的拓扑结构。
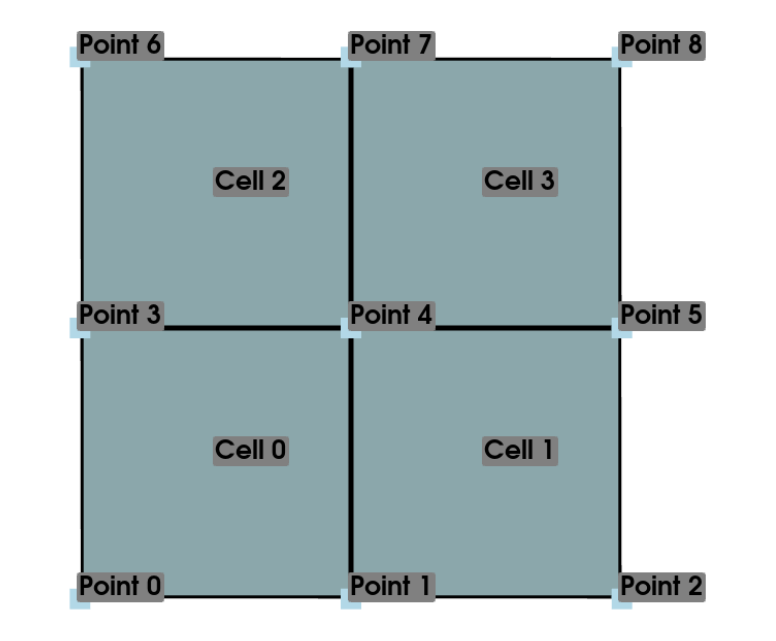
而后,引入不同的属性:
- point_data:包含与数据集中的每个点相关的标量或向量数据,常用于存储点的属性(如温度、速度、密度等),通常用于流场模拟等应用。
- cell_data:包含与数据集中的每个单元格相关的数据,通常用于存储单元格的属性(如应力、体积、标量场值等),适用于有限元分析或网格基准计算。
- field_data:存储与整个数据集相关的全局数据,通常用于存储标量值、数组或其他描述全域特性的信息,例如仿真设置、网格大小或模拟时长等。
一个使用 point data的例子:
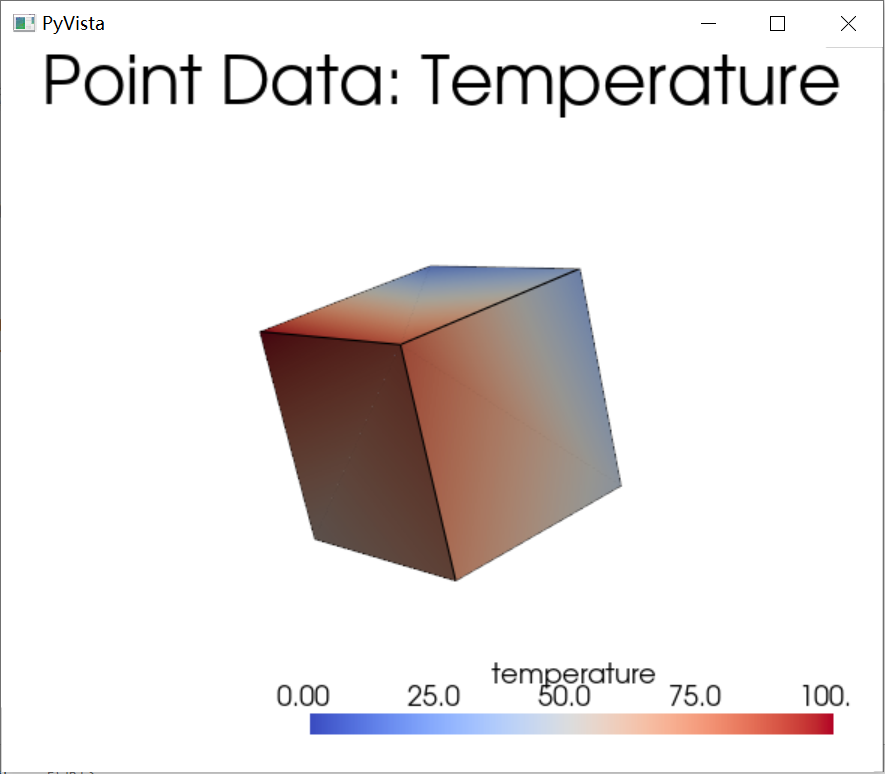
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | |
参考
- https://docs.pyvista.org/api/utilities/geometric
- https://docs.pyvista.org/api/utilities/parametric
- https://docs.pyvista.org/user-guide/data_model
- https://docs.pyvista.org/user-guide/what-is-a-mesh