前面接触到了用于注解的 Path、Query、Body、Field、Form、File、UploadFile、Cookie和Header等,接下来看看依赖注入机制。
内容小记:
- 依赖注入基本用法、依赖项嵌套、路径装饰器依赖项与全局依赖项
- 使用依赖注入例子: HTTP Basic,OAuth2 Passwod Bearer
- 身份认证与授权的零散知识点
注:本文代码在python3.11下验证
依赖注入(Dependency Injection)
FastAPI提供一个非常强大又直观的依赖注入系统。
依赖注入可用于
- 复用相同的逻辑代码(共享业务逻辑)
- 共享数据库连接
- 实现安全、验证、角色权限
- ...
创建依赖项(Dependency/Dependable)
依赖项就是一个函数,它可以使用与路径操作函数相同的参数
| async def common_params(q: str | None = None, limit: int = 100):
return {"q": q, "limit": limit}
|
这个函数可以使用async def 或普通的 def进行定义。
使用依赖项
用法上和Path、Query、Body、Header 等有些像,只不过这儿使用Depends对类型进行注解。
注意:Depends接受一个参数,且该参数必须是可调用对象,比如函数。该函数接收的参数和路径操作函数的参数一样。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 | from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
async def common_params(q: str | None = None, limit: int = 100):
return {"q": q, "limit": limit}
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(commons: Annotated[dict, Depends(common_params)]):
return commons
@app.get("/users/")
async def read_users(commons: Annotated[dict, Depends(common_params)]):
return commons
|
这样一来,如下URL都是合法地址
- localhost:8001/users/?q=2222&limit=10
- localhost:8001/items/?q=2222&limit=10
使用类作为依赖项
除了可调用对象外,类可以直接作为依赖项:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 | from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
class CommonParams:
def __init__(self, q: str | None = None, limit: int = 100):
self.q = q
self.limit = limit
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(commons: Annotated[CommonParams, Depends(CommonParams)]):
return {"q": commons.q, "limit": commons.limit}
@app.get("/users/")
async def read_users(commons: Annotated[CommonParams, Depends(CommonParams)]):
return {"q": commons.q, "limit": commons.limit}
|
工作方式
接收到新的请求时,FastAPI 执行如下操作:
- 用正确的参数调用依赖项函数
- 获取函数返回的结果
- 把函数返回的结果赋值给路径操作函数的参数(例子中 commons 变量的值就是依赖项函数的返回值)。
类型别名
使用Python的类型别名,上面的代码可以这么简化:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 | from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
async def common_params(q: str | None = None, limit: int = 100):
return {"q": q, "limit": limit}
CommonsDep = Annotated[dict, Depends(common_params)]
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(commons: CommonsDep):
return commons
@app.get("/users/")
async def read_users(commons: CommonsDep):
return commons
|
依赖注入嵌套
依赖项可以层层嵌套,就像下面这样,和前面例子的效果一样:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 | from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
async def get_q(q: str | None = None):
return q
async def get_limit(limit: int = 100):
return limit
async def common_params(q: Annotated[str, Depends(get_q)], limit: Annotated[int, Depends(get_limit)]):
return {"q": q, "limit": limit}
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(commons: Annotated[dict, Depends(common_params)]):
return commons
@app.get("/users/")
async def read_users(commons: Annotated[dict, Depends(common_params)]):
return commons
|
每个依赖项的参数都和路径处理函数的参数处理方式是一样的。
路径装饰器中使用依赖项
如果依赖项没有返回值,或者不需要使用依赖项的返回值的话,可以在路径装饰器里面直接指定dependencies:
| from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, HTTPException
app = FastAPI()
async def verify_params(q: str, limit: int = 5):
if len(q) > limit:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="q is too long")
@app.get("/items/", dependencies=[Depends(verify_params), ])
async def read_items():
return {"message": "valid item"}
|
- localhost:8001/items/?q=122
- localhost:8001/items/?q=122456
全局依赖项
如果所有路径函数都需要,可以设置成全局依赖项
使用 FastAPI 的 dependencies 参数
| from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, HTTPException
async def verify_params(q: str, limit: int = 5):
if len(q) > limit:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="q is too long")
app = FastAPI(dependencies=[Depends(verify_params), ])
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items():
return {"message": "valid item"}
|
依赖项在授权与认证上的使用
HTTP Basic 示例
看一下,最简单的HTTP Basic认证过程
例子1
简单的例子,只提示用户输入凭证信息,后台不做验证。
- 路径函数中使用
HTTPBasicCredentials 类型的变量 credentials,用来获取用户凭证信息
- 使用
Depends(HTTPBasic()) 进行注解
| from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI
from fastapi.security import HTTPBasic, HTTPBasicCredentials
app = FastAPI()
security = HTTPBasic(realm="1+1=10")
@app.get("/")
def read_current_user(credentials: Annotated[HTTPBasicCredentials, Depends(security)]):
return {"username": credentials.username, "password": credentials.password}
|
用户输入用户名密码,其被浏览器缓存。清理操作:
- Firefox:
about:preferences#privacy 中 “历史记录” 中的 “登录状态”
- Chrome:
chrome://settings/clearBrowserData 中 Cookie及其他网站数据
- Edge:
edge://settings/clearBrowserData 中的 passwords
例子2
使用Depends的嵌套能力,将用户名和密码的核验功能写成一个依赖项,并作为通过Depends让路径函数使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 | from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, HTTPException
from fastapi.security import HTTPBasic, HTTPBasicCredentials
app = FastAPI()
security = HTTPBasic(realm="1+1=10")
def get_current_username(credentials: Annotated[HTTPBasicCredentials, Depends(security)]):
if credentials.username == "debao" and "oabed" == credentials.password:
return credentials.username
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Invalid username or password", headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Basic"})
@app.get("/")
def read_current_user(username: Annotated[str, Depends(get_current_username)]):
return {"username": username}
|
例子3
前面直接用 ==进行字符串比较,不同字符串比较时间不同,容易被Timing Attacks攻击。比如debao==3ebao和debao==deba3,前者比较后者快。
为避免问题,需要使用python标准secrets库中的compare_digest来进行恒定时间(constant-time compare)比较:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 | from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, HTTPException
from fastapi.security import HTTPBasic, HTTPBasicCredentials
import secrets
app = FastAPI()
security = HTTPBasic(realm="1+1=10")
def get_current_username(credentials: Annotated[HTTPBasicCredentials, Depends(security)]):
if secrets.compare_digest(credentials.username, "debao") and secrets.compare_digest(credentials.password, "oabed"):
return credentials.username
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Invalid username or password", headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Basic"})
@app.get("/")
def read_current_user(username: Annotated[str, Depends(get_current_username)]):
return {"username": username}
|
OAuth2 Password Bearer 示例
- RFC 6749定义了OAuth2框架。OAuth2 有四种授权模式,password是其中一种,用于对客户端高度信任的场合,使用密码申请令牌。
- RFC 6750 示范了一种access token的具体用法,符合这种具体用法的access token统称为Bearer token。注:Bearer token不是一种token值的格式,而是一种规范的用法。
FastAPI例子:
备忘:身份认证与授权
英文中这两个词语。挺像
- authentication
/ ɔːˌθentɪˈkeɪʃn /:身份认证、验证。
- authorization
/ˌɔːθəraɪˈzeɪʃ(ə)n /:授权、批准。
前者用于确定身份,确定你是不是张三。后者已经知道你是张三,需要看你是否由做xxx的权限。
简单来说,认证是验证你的身份的过程,而授权是验证你有权访问的过程。
在HTTP中,相关的状态码:
- 401 Unauthorized。有人说,这个地方HTTP一开始就用错了,应该是未认证Unauthenticated。
- 404 Forbidden。有人说,这个应该叫Unauthorized,认证通过了,但是没有权限。
概念
OAuth2
- OAuth2:这是一个规范,定义了几种处理身份认证的和授权的方法。它包含了使用第三方进行身份认证的方法。网上可见的 使用Google、Github、Twitter 登录 的背后机制。
- OAuth1:很复杂,没有被广泛使用。它包含了加密通讯的规范。
- OpenID Connect:一个基于OAuth2的认证规范。Google在使用它。
RFC 6749定义了OAuth2框架,RFC 6750 示范了一种access token的具体用法,符合这种具体用法的access token统称为Bearer token。注意:Bearer token不是一种token值的格式,而是一种规范的用法。
OAuth2的流程如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 | +--------+ +---------------+
| |--(A)- Authorization Request ->| Resource |
| | | Owner |
| |<-(B)-- Authorization Grant ---| |
| | +---------------+
| |
| | +---------------+
| |--(C)-- Authorization Grant -->| Authorization |
| Client | | Server |
| |<-(D)----- Access Token -------| |
| | +---------------+
| |
| | +---------------+
| |--(E)----- Access Token ------>| Resource |
| | | Server |
| |<-(F)--- Protected Resource ---| |
+--------+ +---------------+
Figure Abstract Protocol Flow
|
OAuth2 在 客户端(Client)与 资源服务器之间,设置了一个授权服务器(authorization server)。客户端不能直接登录服务提供商,只能登录授权服务器。客户端登录授权服务器所获得的令牌(token)用于登录资源服务器。
令牌(token)与密码(password)的作用是一样的。但是:令牌是短期的,到期会自动失效,用户自己无法修改。密码一般长期有效,除非用户修改;另外,令牌可以设置权限范围。
OAuth2 有4种授权模式:
- 授权码(authorization code):最常用的流程,安全性最高。先申请授权码,在利用该码获取令牌。
- 隐含模式(implicit):跳过授权码,直接请求颁发令牌
- 密码模式(resource owner password credentials):用于对客户端高度信任的场合,使用密码申请令牌。
- 客户端凭证(client credentials):没有前端,在命令行下申请令牌
Bearer令牌传给资源服务器有三种方式
- Authorization Header 该头部定义与Basic方案类似(服务端必须支持):
| GET /resource HTTP/1.1
Host: server.example.com
Authorization: Bearer mF_9.B5f-4.1JqM
|
- Form-Encoded Body Parameter:
| POST /resource HTTP/1.1
Host: server.example.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
access_token=mF_9.B5f-4.1JqM
|
- URI Query Parameter(不建议):
| GET /resource?access_token=mF_9.B5f-4.1JqM HTTP/1.1
Host: server.example.com
|
如果请求中没有token信息,资源服务器响应
| HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
WWW-Authenticate: Bearer realm="example"
|
Bearer令牌响应
| HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
Cache-Control: no-store
Pragma: no-cache
{
"access_token":"mF_9.B5f-4.1JqM",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":3600,
"refresh_token":"tGzv3JOkF0XG5Qx2TlKWIA"
}
|
Http认证
HTTP的认证框架由RFC7235定义,它是多种认证scheme的基础。其中:
- Basic 由RFC7617定义。
- Bearer 由RFC6750定义
- Digest 由 RFC7616定义
- ...
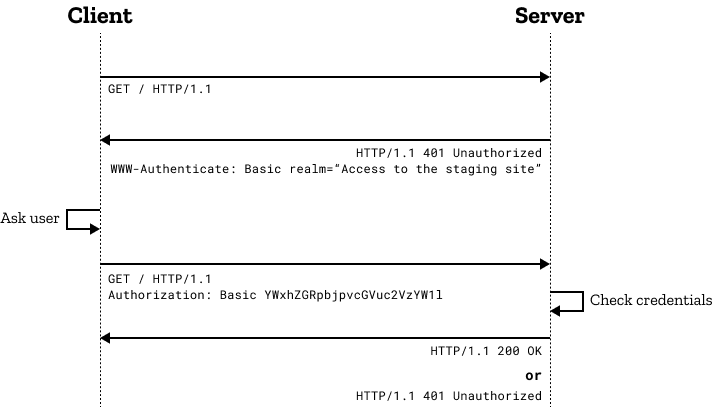
以Basic为例,看看流程:
- 服务端:你访问的页面需要基本认证,请提供用户名和密码。Basic说明支持基本认证,realm说明需要这个安全区的用户名和密码。
| HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="debao site"
|
- 客户端:提示用户输入用户名密码(比如
aladdin:opensesame),而后用base64编码并告知服务端:
| GET / HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Basic YWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuc2VzYW1l
|
- 服务端:进行验证操作,没问题返回正常页面,否则继续提示需要凭证。
OpenAPI
FastAPI基于OpenAPI。
OpenAPI是用于构建API的开放规范,它定义了多个安全方案的方法:
- apiKey:一个密钥,可来自查询参数、请求头、cookie
- http:标准的HTTP身份认证系统,包括bearer,HTTP Basic,HTTP Digest 等。
- oauth2
- openIdConnect
参考
- https://fastapi.tiangolo.com
- https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/
- https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/security/
- https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/dependencies/
- https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/advanced/security/http-basic-auth/
- https://codahale.com/a-lesson-in-timing-attacks/
- https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7235
- https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7617
- https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc6750
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Authentication
- https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2019/04/oauth_design.html
